1. MSCA Mobility rule
To be eligible for this PhD position, applicants must not have resided or carried out their main activity (work, studies, etc.) in the United Kingdom (country of the recruiting beneficiary) for more than 12 months during the 36 months immediately preceding the recruitment date — unless this was part of a compulsory national service or a procedure for obtaining refugee status under the Geneva Convention.
2. Description of the Work Project
Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) services underpin critical infrastructure across transportation,
telecommunications, energy, and defense. However, traditional PNT systems—primarily reliant
on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)—face growing vulnerabilities from signal jamming,
spoofing, and environmental obstructions like urban canyons or dense foliage. These threats highlight
the urgent need for resilient alternatives that can maintain service continuity under adverse
conditions. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Signals of Opportunity (SoOp) offer a compelling solution by repurposing
signals from non-navigation satellites, such as those used for communications or Earth observation.
With their lower altitude, stronger signal strength, and rapid orbital movement, LEO SoOp
can enhance coverage, reduce latency, and provide redundancy, making them a vital component in
building robust, next-generation PNT architectures.
Despite its promise, delivering reliable PNT services from LEO Signals of Opportunity presents several
complex research challenges. First, the non-dedicated nature of SoOp signals means they were
not designed for navigation, leading to variability in signal structure, timing, and availability that
complicates receiver design and signal processing. Additionally, the rapid motion of LEO satellites
introduces high Doppler shifts and frequent handovers, requiring sophisticated tracking algorithms
and real-time adaptation. Developing adequate receivers co-designed with the signal processing algorithms
is another open problem. Ensuring precise orbit and clock knowledge of the signal sources
is another hurdle. Furthermore, integrating LEO SoOp into existing PNT frameworks demands robust
fusion techniques to reconcile data from disparate sources while maintaining accuracy and integrity.
3. Core activities
- Define a use case for PNT services using the Signal of Opportunity from LEO satellites and identify technological bottlenecks based on the performance requirements and current state-of-the-art
- Investigate techniques and methodologies to address the identified challenges
Research field:
- Electrical engineering
- Computing engineering
Required skills:
- Embedded systems
- System engineering
- Reliability concepts
- Electro-thermal-mechanical concepts
- Numerical simulation programming (e.g., Python, Matlab, C++, …)
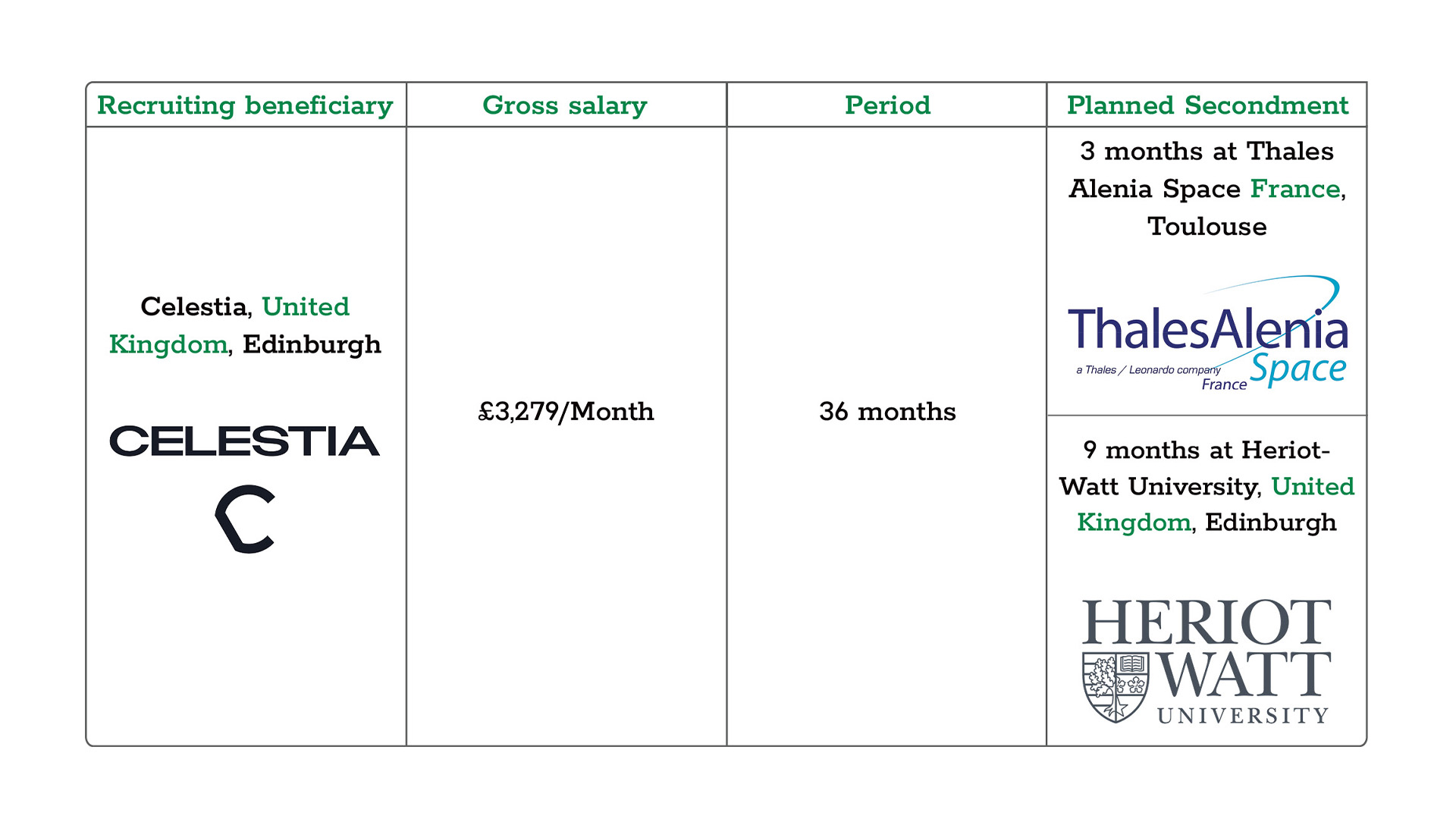
4. Recruitment and secondment plan: